How to Hire a Scala Developer: Step-by-Step
Table of Contents
Follow this expert guide to hire a reliable Scala developer for your big data or distributed systems project. Read more tips in our blog.
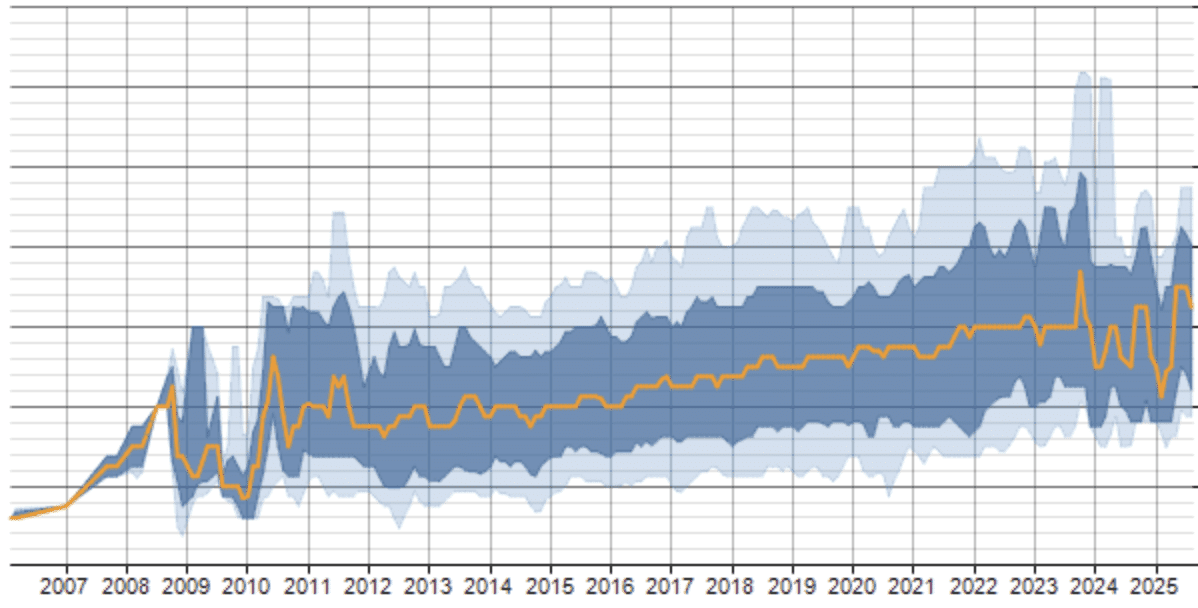
2025 Scala Trend
Scala demand in big data grew 35% due to Spark integration—perfect for AI and fintech (LinkedIn, 2025).
1. Define Your Project Needs
Determine if you need a Scala developer for functional programming (Cats Effect), big data (Spark), or distributed systems (Akka). Specify scope, timeline, and budget. Example: Need a Spark developer for a 4-month data analytics project, $10,000 budget.2. Write a Clear Job Description
A strong job post attracts top Scala talent. Example:- Title: Senior Scala Developer (Spark)
- Role: Build scalable data pipelines for analytics platform.
- Skills: Scala, Spark, Akka, SBT, Git; Kafka a plus.
- Rate: $80-120/hour, remote.
3. Interview Effectively
Ask targeted questions to assess Scala expertise:- Question: “How do you use Scala’s type system to prevent errors?”
Good Answer: Mentions type safety, pattern matching, or algebraic data types for robust code. - Question: “Explain how you’d optimize a Spark job.”
Good Answer: Discusses partitioning, caching, or broadcast variables to reduce shuffle costs. - Question: “How do you handle concurrency in Akka?”
Good Answer: Explains actors, message passing, and supervision strategies.
4. Avoid Common Pitfalls
Steer clear of these mistakes:- Overlooking Functional Skills: Ensure expertise in Scala’s functional paradigms.
- Unclear Scope: Define deliverables to avoid delays (e.g., “Build a Spark pipeline”).
- Cost-Only Focus: Low rates may lead to inexperienced hires.
- Ignoring Team Fit: Verify communication and Agile experience.
Expert Insight
“Scala developers excel in complex systems, but you need to test their functional programming skills and framework knowledge to ensure they can deliver scalable solutions.” – Elena V., Senior Recruiter at HireJS Guide
Post Hiring Support (Extra offer):
- Technical Oversight: Optional supervision to ensure your Scala developer aligns with project goals, such as maintaining type safety or optimizing Spark jobs.
- Tooling and Integration Support: Guidance on integrating Scala with your existing stack, like setting up Kafka streams or deploying with Docker.
- Ongoing Assistance: Our team is available to resolve issues, from debugging complex monadic chains to coordinating with your in-house engineers.
Table of Contents
Talk to Our Expert
Our journey starts with a 30-min discovery call to explore your project challenges, technical needs and team diversity.

Yaroslav Kuntsevych
co-CEO



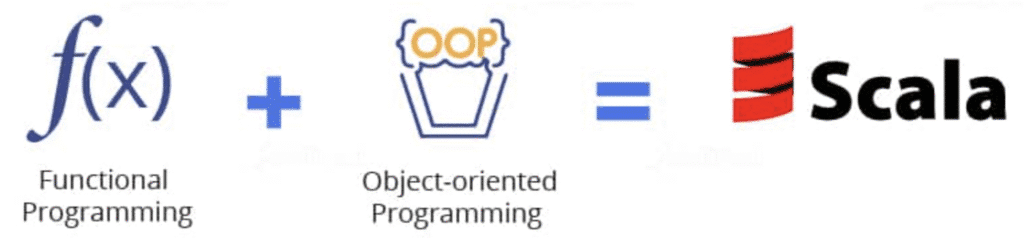 In its functional paradigm, developers use immutable data, higher-order functions, and concepts like monads, functors, and applicatives to write concise, predictable code. For example, libraries like Cats and Scalaz enable functional programming patterns for handling side effects or composing computations. In its object-oriented paradigm, Scala uses traits, classes, and objects to support encapsulation and inheritance, with features like mixins for flexible code reuse. This dual nature allows Scala engineers to choose the best approach for the task—functional for data pipelines with Spark, or object-oriented for modular backend systems with Play. This flexibility makes Scala ideal for projects requiring both scalability and maintainability, such as real-time analytics or distributed APIs.
In its functional paradigm, developers use immutable data, higher-order functions, and concepts like monads, functors, and applicatives to write concise, predictable code. For example, libraries like Cats and Scalaz enable functional programming patterns for handling side effects or composing computations. In its object-oriented paradigm, Scala uses traits, classes, and objects to support encapsulation and inheritance, with features like mixins for flexible code reuse. This dual nature allows Scala engineers to choose the best approach for the task—functional for data pipelines with Spark, or object-oriented for modular backend systems with Play. This flexibility makes Scala ideal for projects requiring both scalability and maintainability, such as real-time analytics or distributed APIs.